Introduction
Almost one hundred years ago, Henry Ford, the man behind the Ford Motor Company, imagined an "energy currency", suggesting that instead of gold, nations could base their currencies on energy resources. While this idea never materialised - probably due to its potential to undermine government control over wealth- Ford's concept is partly reflected in bitcoin.
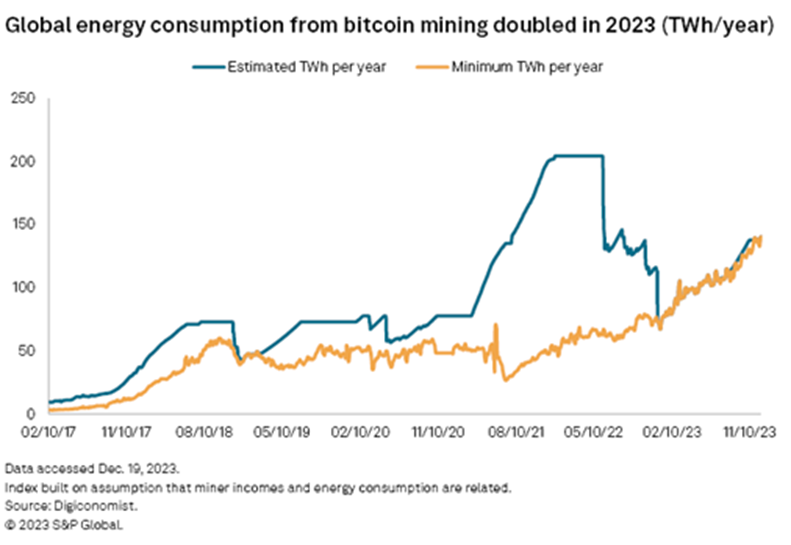
This cryptocurrency, often referred to as digital gold, operates on a decentralised network and is created via a "mining" process that requires a significant amount of energy. Indeed, some argue that the value of bitcoin is intrinsically linked to the energy expended in its creation.
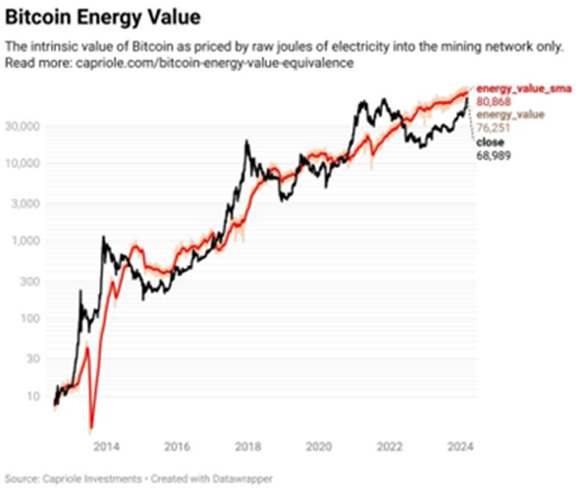
Capriole Investments developed the "Energy Value Equivalence" model, which calculates the value of bitcoin based on its energy consumption. According to this model, bitcoin's intrinsic value is higher than its current price.
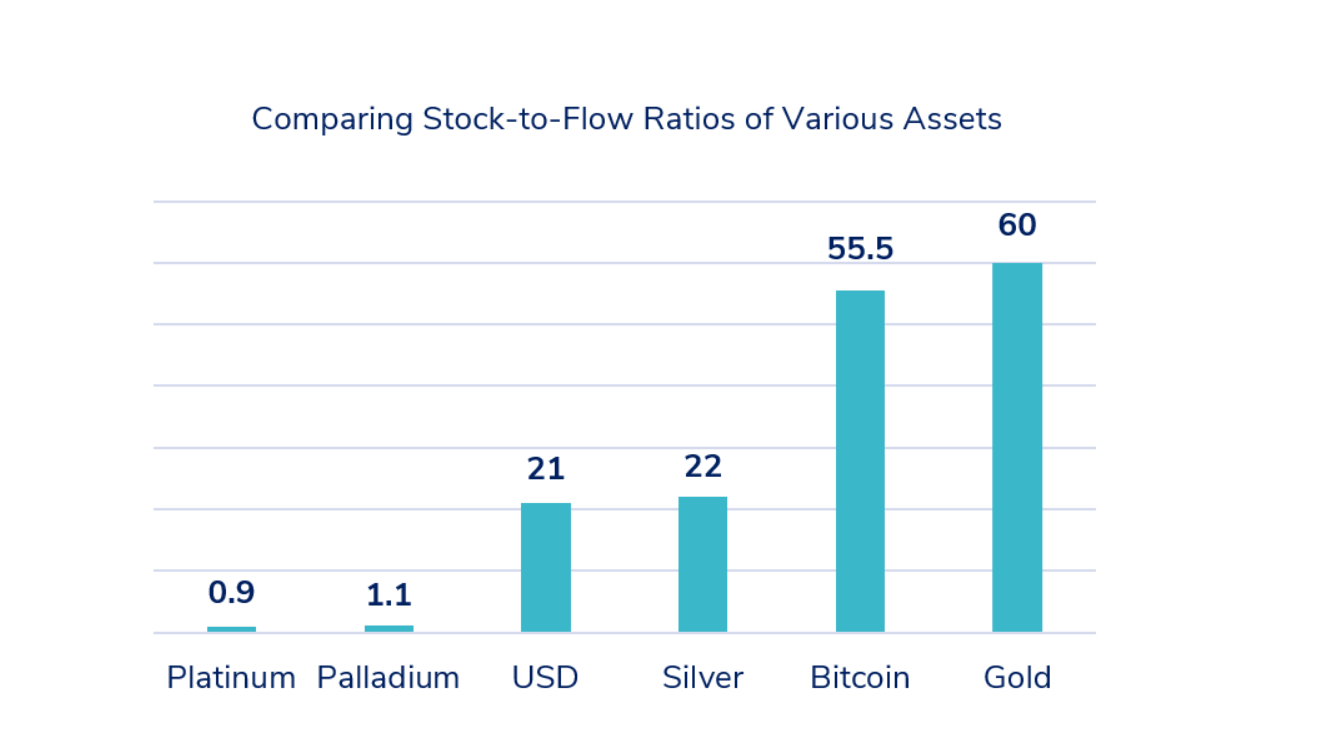
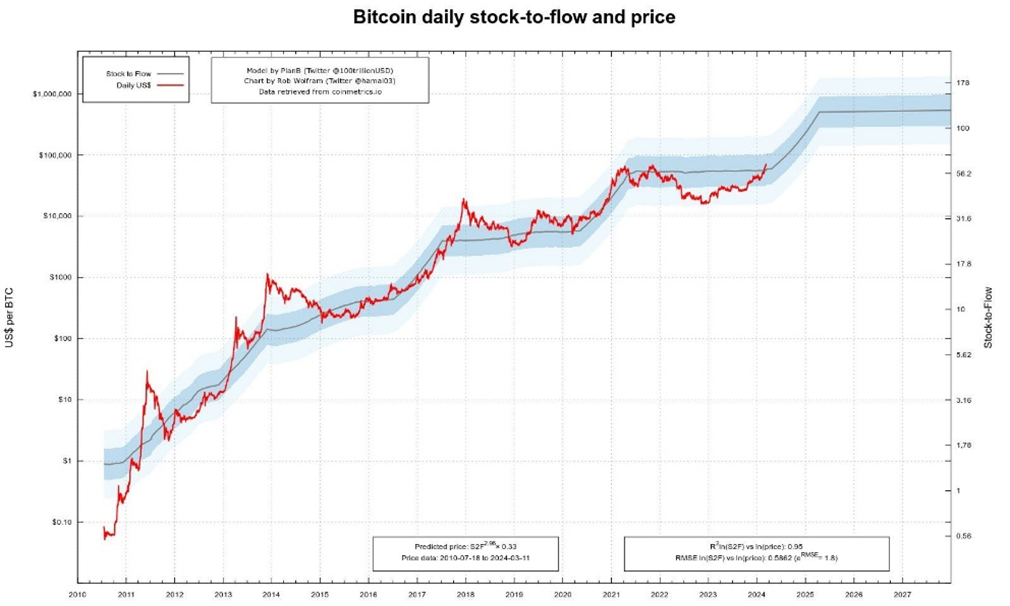
Another valuation model for bitcoin is the "stock-to-flow" ratio, which assesses its scarcity by comparing existing supply with annual production. This model has attracted considerable interest for its ability to accurately predict bitcoin's price movements.
The two above models offer distinct but complementary perspectives, highlighting the dynamics driving bitcoin's appreciation. Overview below.



.png)