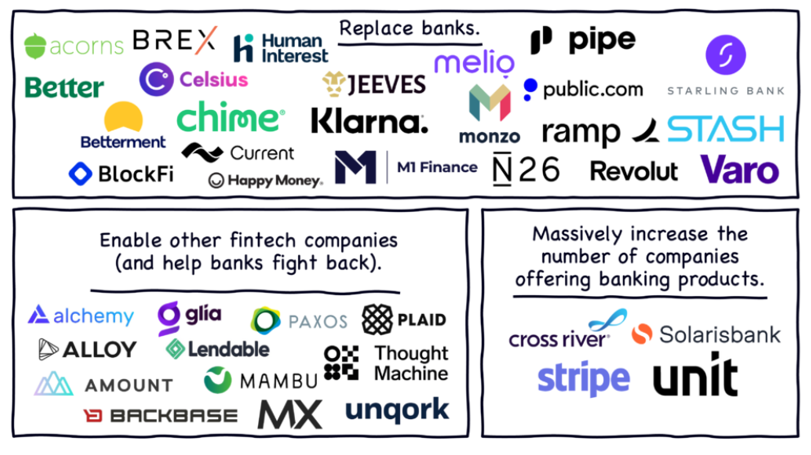
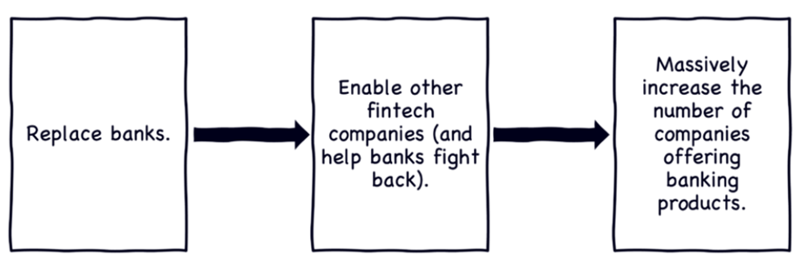
1. Embedded payments
This is the most-well known type of embedded financial offerings. This form of embedded finance has gained widespread recognition and adoption, with major players like Amazon, Uber, DoorDash, and Walmart. Apps such as Google Pay, Apple Pay and Venmo are examples of simplified payment solutions that enable users to store their financial data and carry out transactions seamlessly within a common interface.
In this way, businesses enable customers to place orders and pay directly on the same app. Users no longer need to re-enter credit card details or rely on third-party platforms to process payments securely. The main benefit for customers lies in the seamless payment experience and the elimination of friction points.
To illustrate the effectiveness of integrated payments, let's take the example of the Starbucks app. Starbucks not only securely stores payment information, but also encourages customers to participate in a loyalty program that allows them to earn points using the app. Such integrations enhance the user experience by providing a simple and attractive payment process.
2. Embedded buy now, pay later installment plans.
Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) enables retailers to offer their customers access to credit directly through their e-commerce applications. BNPL works like an installment plan, allowing customers to spread the total cost of a purchase over several payments over a set period.
By opting for the merchant's BNPL option, customers take out a small loan to pay for their purchase. They then makes payments for the chosen product or service over several weeks, usually at zero interest. Simultaneously, the retailer receives full payment for the total cost of the purchase, while the BNPL provider collects the customer's funds on pre-agreed due dates.
Fintech companies such as Klarna and afterpay facilitate this service by providing the necessary technology and data infrastructure and enable their customers to pay using BNPL on a wide range of websites, including those of Nike, Valentino and JBL.
3. Embedded lending
Embedded lending enables companies to offer loans directly on their platforms, without using traditional financial institutions, saving customers the hassle of having to seek out separate financial services.
Through partnerships with fintech companies, these businesses can offer their customers various financing options, including installment plans, "Just in time lending" and BNPL schemes, as mentioned above.
Customers can access these lending services directly on the company's app or website, without having to navigate the traditional banking system.
Stride Funding, for example, is a fintech offering alternative financing solutions for students and families. Its models include income-sharing and employer-sponsored loans, and deferred tuition agreements.



.png)