Straight from the Desk
Syz the moment
Live feeds, charts, breaking stories, all day long.
- All
- equities
- United States
- Macroeconomics
- Food for Thoughts
- markets
- Central banks
- Fixed Income
- bitcoin
- Asia
- europe
- investing
- geopolitics
- gold
- technical analysis
- Commodities
- Crypto
- AI
- Technology
- nvidia
- ETF
- earnings
- Forex
- china
- Real Estate
- oil
- banking
- Volatility
- energy
- magnificent-7
- apple
- Alternatives
- emerging-markets
- switzerland
- tesla
- United Kingdom
- Middle East
- assetmanagement
- amazon
- microsoft
- russia
- ethereum
- ESG
- meta
- Industrial-production
- bankruptcy
- Healthcare
- Turkey
- Global Markets Outlook
- africa
- Market Outlook
- brics
- performance
🚨 Germany’s biggest carmaker is in trouble.
Volkswagen is staring at a potential €11 billion cash shortfall next year — a gap big enough to derail its investment plans and EV transition. Half-year profits are down 33%, and cash flow has turned negative (€1.4 billion). What’s driving the crisis? 🇨🇳 Weak sales in China 🇺🇸 Tariffs from the U.S. ⚙️ Fierce competition from fast-moving Chinese EV makers Now, cuts are hitting everywhere — marketing, sales, and even R&D. The company may be forced to sell assets just to fund new models and technologies. Executives are calling it “particularly fatal” — hitting right as Volkswagen tries to shift from combustion engines to electric. The once-unshakable German auto powerhouse is learning the hard way: 🔋 The EV race isn’t just about innovation — it’s about survival. Source: https://lnkd.in/gC5NC2YH, Bild
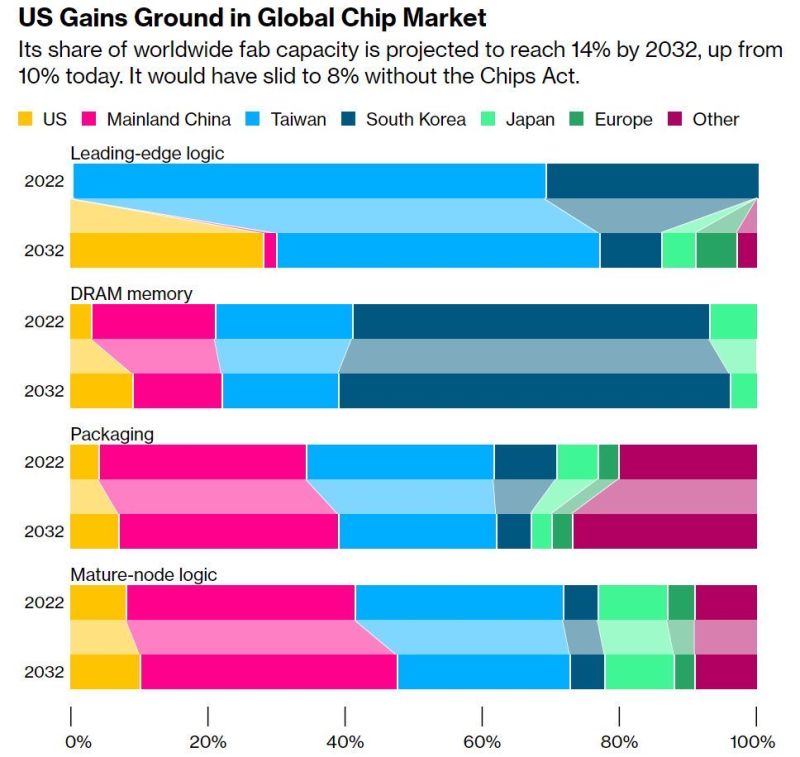
Europe is basically not participating in chips manufacturing, even worse with rare earths.
Should there be a geopolitical event in Asia, what will happen to the European economy ??? Source: Michel A,Arouet
Should it be be called Standard & Europoor‘s 500 ?
Source: Michel A.Arouet
In August '25, German industrial production collapsed 4.3% m/m.
Germany is headed for the third consecutive recession year. To Dr Polleit, the "Great Reset" is destroying industrual production and economic growth in Germany. ➡️ Polleit is a German economist affiliated with the Austrian School of economics, and president of the Ludwig von Mises Institut Deutschland. Mises Institute. He is strongly skeptical of state intervention, central banking, fiat money, and what he sees as coercive economic planning ➡️Polleit general critiques on Germany are the following: 👉 Heavy regulation, strong state involvement 👉Germany’s ambitious transition from fossil fuels to renewables may cause disruptions in energy supply, cost volatility, grid stresses, and increase production costs 👉Export dependence and global competition 👉Monetary and fiscal pressures reduce real returns on capital and discourage long-term investment. 👉Uncertainty and investment risk 👉With more government programs, state investment, subsidies, and oversight, private actors may be crowded out or discouraged. Polleit would claim that entrepreneurship and innovation decline. 👉Central planning or incentive distortions lead to misallocation of capital. Polleit warns that “green subsidies” or mandated transitions may favor politically connected actors rather than the most efficient ones. 🚨 Hence, under Polleit’s logic, Germany — already having high regulation, energy transition burdens, export dependency, and significant state involvement — would be particularly vulnerable to further growth suppression from Great Reset-type policies. He would argue that growth is slowly being “destroyed” by compounding layers of regulatory, monetary, and fiscal drag. Source: Thorsten Polleit @ThorstenPolleit on X
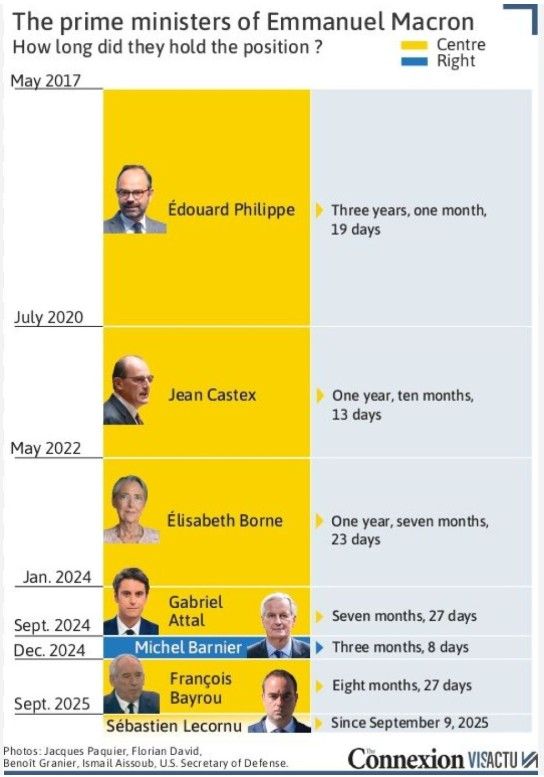
France changes its Prime Ministers more often than some people buy new underwear...
Source: Connexion VisActu
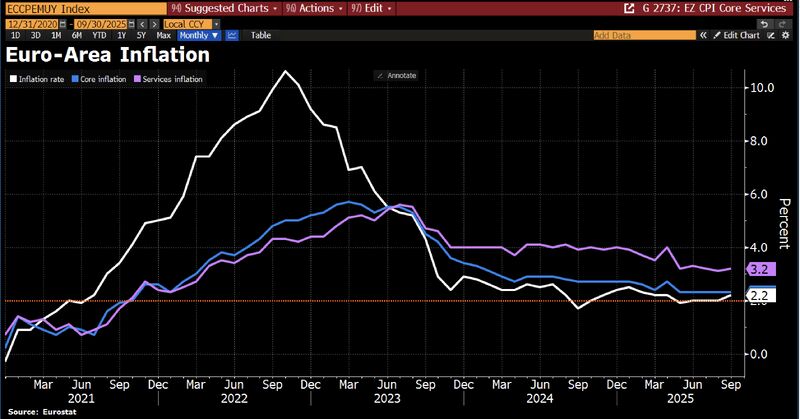
In case you missed it... Eurozone inflation picked up in Sep, with CPI rising 2.2% YoY, driven by hashtag#energy base effects and higher service costs.
Core inflation, which excluding volatile items like energy & food, remained steady at 2.3%, in line with expectations. Source: Bloomberg, HolgrZ
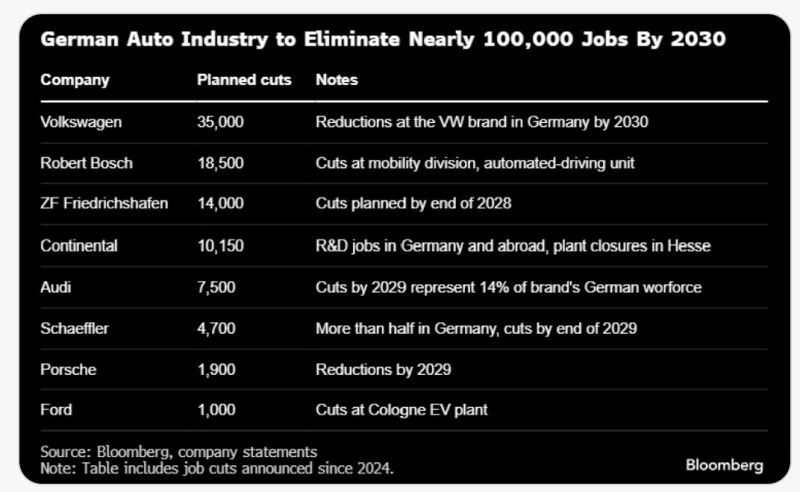
The German auto industry is expected to eliminate nearly 100,000 jobs by 2030.
Carmakers and their suppliers are struggling w/waning demand, high labor & energy costs & intensifying competition from Chinese manufacturers. Overall, Germany’s auto sector has lost roughly 55,000 jobs over the past 2yrs. Tens of thousands of additional positions are set to disappear by 2030, in an industry that employs more than 700,000 people. Source: HolgerZ, Bloomberg
In Germany, the short-lived rally at the start of the year has already fizzled out.
The country is losing ground on the global stage: German stocks now make up just 2.1% of global market capitalization, down from 2.4% only three months ago. Source: Bloomberg, HolgerZ
Investing with intelligence
Our latest research, commentary and market outlooks