Straight from the Desk
Syz the moment
Live feeds, charts, breaking stories, all day long.
- All
- us
- macro
- equities
- Food for Thoughts
- sp500
- Central banks
- Bonds
- markets
- bitcoin
- Asia
- technical analysis
- investing
- europe
- Crypto
- geopolitics
- tech
- performance
- gold
- Commodities
- AI
- nvidia
- ETF
- earnings
- Forex
- Real Estate
- oil
- banking
- magnificent-7
- Volatility
- nasdaq
- apple
- emerging-markets
- energy
- china
- Alternatives
- switzerland
- tesla
- trading
- sentiment
- russia
- Money Market
- assetmanagement
- UK
- ESG
- Middle East
- microsoft
- amazon
- ethereum
- meta
- bankruptcy
- Turkey
- Healthcare
- Industrial-production
- Global Markets Outlook
- africa
- brics
- Market Outlook
- Asset Allocation Insights
- Flash
- Focus
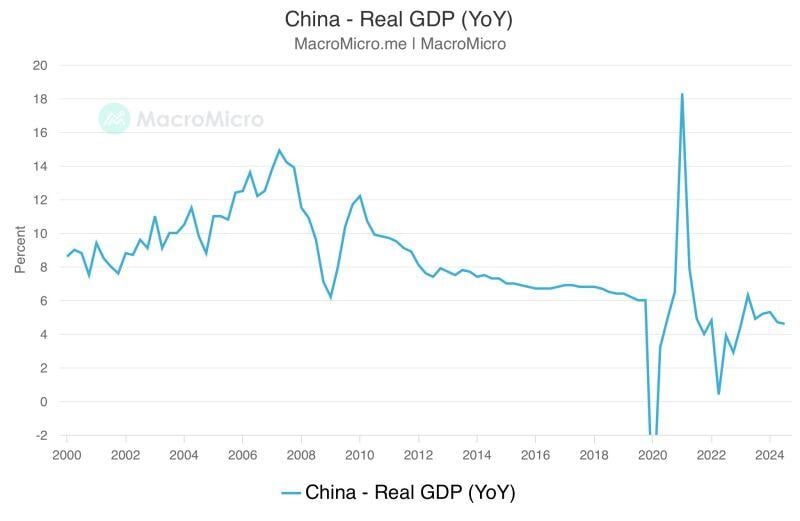
China's Q3 GDP hits weakest pace since early 2023, backs calls for more stimulus
China's economy grew at the slowest pace since early 2023 in the third quarter, and though consumption and factory output figures beat forecasts last month a tumbling property sector remains a major challenge for Beijing as it races to revitalise growth. See below key China GDP data: Q3 GDP 4.6% y/y [Est.+4.5%] Q1-Q3 GDP 4.8% y/y [Prev.+5.0%] Sept retail sales 3.2% y/y [Est.2.5%] Sept industrial growth 5.4% y/y [Est.4.5%] Jan-Sept fixed asset investment 3.4% y/y [Est.3.3%] Sept Unemployment 5.1% [Prev. 5.3%] Source: Reuters, MacroMicro
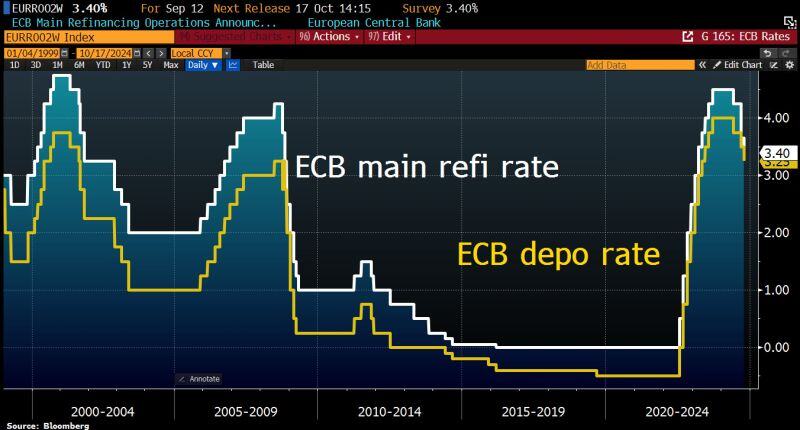
ECB cut the key rates by 25bps as expected.
Depo rate to 3.25%, Main Refi to 3.4%. Guidance is unchanged: ECB to follow data-dependent, Meeting-by-Meeting approach. • Even after this third rate cut of the year, monetary policy remains restrictive in Europe, with the real short-term rate still at a level not seen over the past 15 years. Given the ongoing dynamics in economic activity and inflation, this implies that the ECB will have to continue to lower rates in the coming months, in order to bring its monetary policy to a neutral stance at minimum. Rate cuts at the coming meetings are therefore to be expected, in December and in the course of 2025. Given the worrying trend in economic activity data, an acceleration in the pace of rate cuts, with a possible 50bp cut at the December meeting, cannot be ruled out. If growth in the Eurozone stalls, a faster pace of rate cuts to remove the restrictiveness of the monetary policy, or even to move it into supportive territory, might prove to be warranted. Source chart: Bloomberg
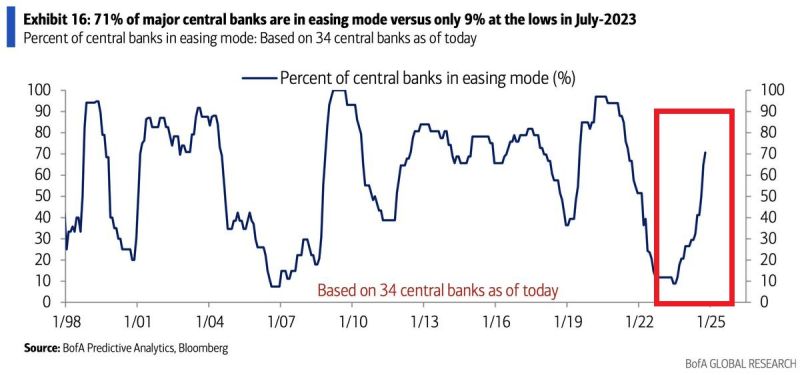
👉 A SYNCHRONIZED GLOBAL MONETARY POLICY EASING
71% of major central banks are now easing their monetary policy, the most since the 2020 CRISIS. This is also in line with the Financial Crisis and the 2001 recession. Source: BofA
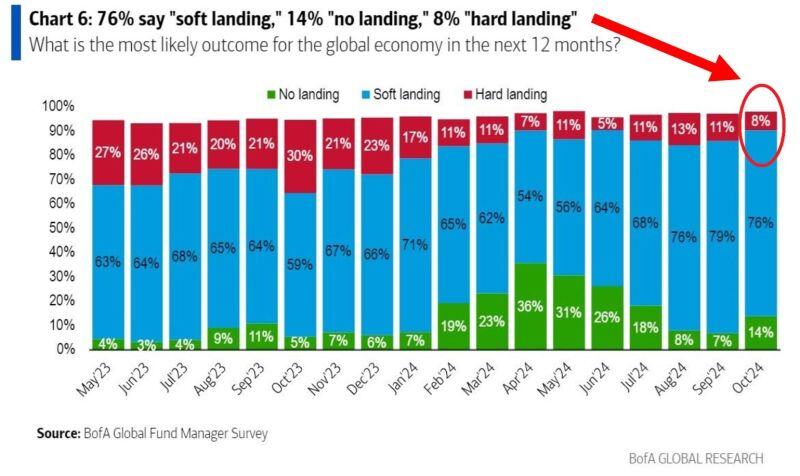
😎 ALMOST NO GLOBAL INVESTORS EXPECT A RECESSION 😎
Only 8% of investors from the BofA survey* expect a hard landing for the global economy within next 12 months, second-lowest reading in 2 years. 76% expect a soft landing. *Survey of 195 participants with $503 billion asset Source: BofA, Global Markets Investor
Between 2000 and 2024:
US Income +24% US House prices +140% Source: Trend Spider
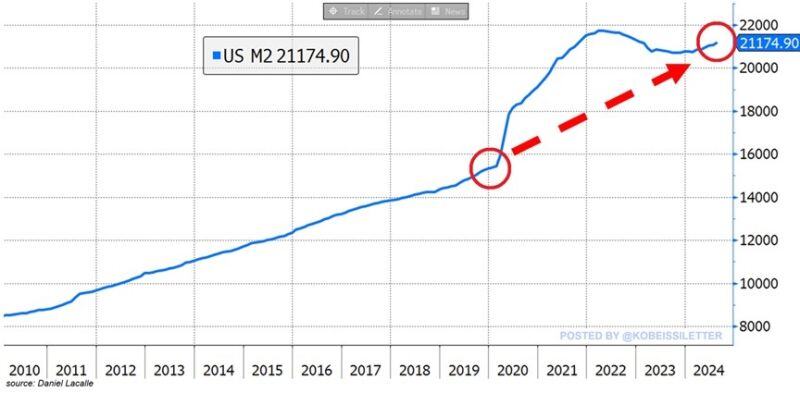
BREAKING: The US money supply hit $21.17 trillion in August, the highest level since January 2023.
This also marks a fifth consecutive monthly increase for the US money supply. Over the last 10 months, the amount of US Dollars in circulation has jumped by a MASSIVE $484 billion. In effect, the money supply is now just $548 billion below a new all-time high. After a brief decline, the quantity of money in the financial system is surging again raising concerns about another inflation wave. Source: The Kobeissi Letter
Investing with intelligence
Our latest research, commentary and market outlooks